Using the Cloud for Backup
Do you need to retain a cloud backup of your data offsite? Managing backups across physical servers, virtual server hosts, VMs’, desktops, laptops and the public cloud is a huge, time consuming job that has to be monitored and tested regularly to ensure all data can be recovered in a timely manner.
Cloud backup is designed to take advantage of using the cloud as a primary or secondary storage location for backing up data. The cloud is an ideal location for storing data as it’s off-site and could become part of your DR strategy.
Where to store backup data?
Careful consideration needs to take place where to store your cloud backups. Should a disaster strike and the requirement to restore multiple terabytes of data the WAN bandwidth could prove to be a stumbling block in trying to restore a server or application in a timely manner. In addition to this transmission costs will also increase accordingly.
Another method would be to store data in a private cloud where you own the cloud storage and are not charged for transmission costs as your backup location could be your local on-premise private cloud that automatically migrates data to your cloud.
The third preferred option is to use backup software that can create a second copy of your data on-premise and a secondary copy stored in the cloud.
If your backup software doesn’t support a second copy or cloud backup you could perform the following using 3rd party replication software or drop-n-drag:
- Create a full backup, once complete upload to your cloud storage
- Every incremental or differential should be uploaded as well thereafter
Backup Methods
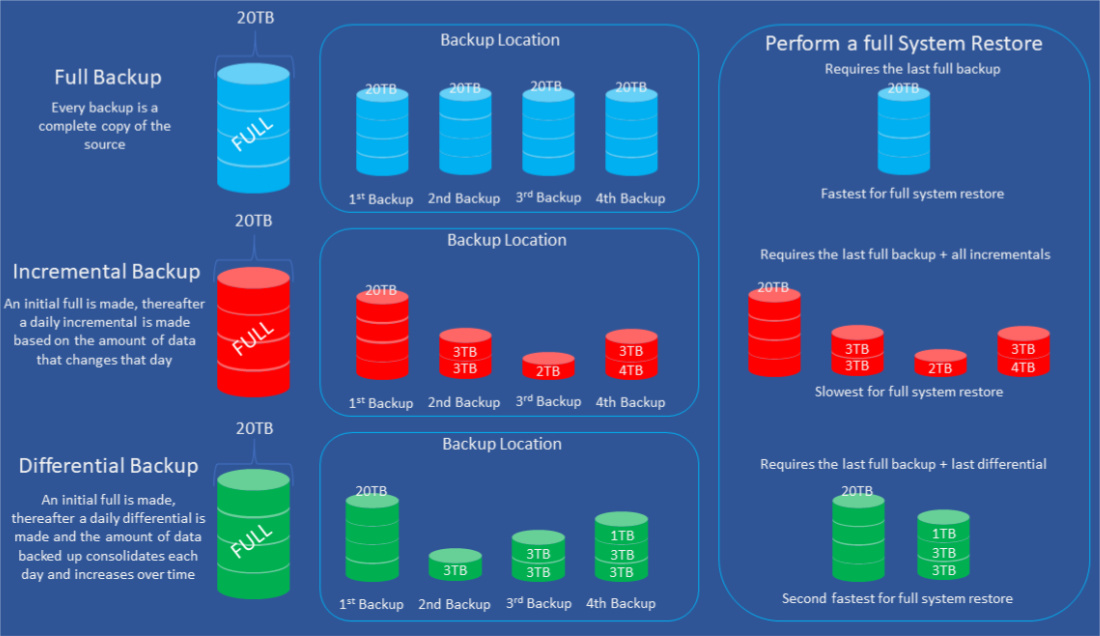
Whilst there are multiple methods to storing your cloud backups, there are primarily three different types of backup and it is important to understand the differences
- Full backups copy the entire data set every time a backup is initiated. This type of backup provides the highest level of protection. Depending on the amount of data backed up could restrict the amount of backup window available or take up too much storage capacity.
- Incremental backups only back up the data that has been changed or updated since the last backup. This method saves time and storage space but can make it more difficult to perform a complete restore. Incremental is a common form of cloud backup because it tends to use fewer resources.
- Differential backups are like incremental backups because they only contain data that has been altered. However, differential backups back up data that has changed since the last full backup, rather than the last backup in general. This method solves the problem of difficult restores that can arise with incremental backups.
Protecting backups from Ransomware
Increasingly many modern backup software packages such as Commvault, Rubrik, VEEAM support the use of immutable storage. Immutable storage or object-lock enables the writing of data to storage that acts as it were WORM (Write Once Read Many). Cloud storage that supports object-lock provides the user with the ability to set a retention period to store the cloud backups, once this has been set that data cannot be changed, modified or deleted until the retention period is up.
If you would like to know how storing data in the cloud can help alleviate or solve some of your issues please call us on 01256 331614 or email save@savedtocloud.com.
Trial our Cloud Storage
Please complete the form found here.
Thanks for reading